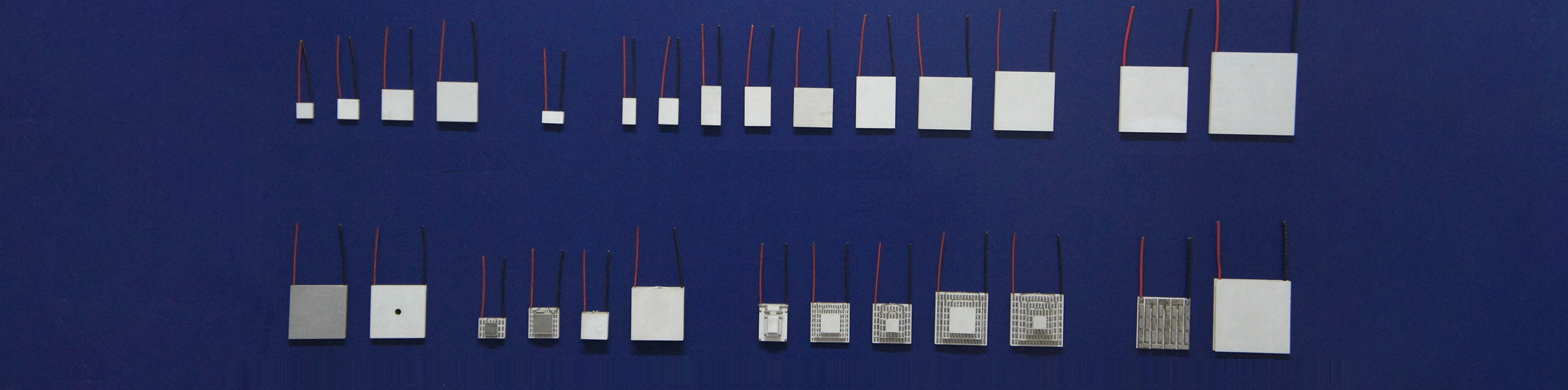
Thermoelectric Modules and Their Application
When choosing a thermoelectric semiconductor N,P elements, the following issues should be determined first:
1. Determine the working state of the thermoelectric semiconductor N,P elements. According to the direction and size of the working current, you can determine the cooling, heating and constant temperature performance of the reactor, although the most commonly used is the cooling method, but should not ignore its heating and constant temperature performance.
2, Determine the actual temperature of the hot end when cooling. Because the thermoelectric semiconductor N,P elements is a temperature difference device, to achieve the best cooling effect, the thermoelectric semiconductor N,P elements must be installed on a good radiator, according to the good or bad heat dissipation conditions, determine the actual temperature of the thermal end of the thermoelectric semiconductor N,P elements when cooling, it should be noted that due to the influence of temperature gradient, the actual temperature of the thermal end of the thermoelectric semiconductor N,P elements is always higher than the surface temperature of the radiator, usually less than a few tenths of a degree, more than a few degrees, ten degrees. Similarly, in addition to the heat dissipation gradient at the hot end, there is also a temperature gradient between the cooled space and the cold end of the thermoelectric semiconductor N,P elements
3, Determine the working environment and atmosphere of the thermoelectric semiconductor N,P elements. This includes whether to work in a vacuum or in an ordinary atmosphere, dry nitrogen, stationary or moving air and the ambient temperature, from which thermal insulation (adiabatic) measures are taken into account and the effect of heat leakage is determined.
4. Determine the working object of the thermoelectric semiconductor N,P elements and the size of the thermal load. In addition to the influence of the temperature of the hot end, the minimum temperature or maximum temperature difference that the stack can achieve is determined under the two conditions of no-load and adiabatic, in fact, the thermoelectric semiconductor N,P elements can not be truly adiabatic, but also must have a thermal load, otherwise it is meaningless.
Determine the number of thermoelectric semiconductor N,P elements. This is based on the total cooling power of the thermoelectric semiconductor N,P elements to meet the temperature difference requirements, it must ensure that the sum of the thermoelectric semiconductor elements cooling capacity at the operating temperature is greater than the total power of the thermal load of the working object, otherwise it can not meet the requirements. The thermal inertia of the thermoelectric elements is very small, no more than one minute under no-load, but because of the inertia of the load (mainly due to the heat capacity of the load), the actual working speed to reach the set temperature is much greater than one minute, and as long as several hours. If the working speed requirements are greater, the number of piles will be more, the total power of the thermal load is composed of the total heat capacity plus the heat leakage (the lower the temperature, the greater the heat leakage).
TES3-2601T125
Imax: 1.0A,
Umax: 2.16V,
Delta T: 118 C
Qmax: 0.36W
ACR: 1.4 Ohm
Size : Base size : 6X6mm, Top size: 2.5X2.5mm, Height : 5.3mm
Post time: Nov-05-2024